Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect any part of the body. The pathophysiology of lupus is still not completely understood, but scientists believe it is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. In this article, we will discuss the different aspects of the pathophysiology of lupus, including how the disease affects other parts of the body and what treatments are currently available.

What Is Lupus?
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect any body part. Lupus symptoms can vary significantly from person to person, ranging from mild to severe. In some cases, lupus can be deadly. There is no cure for lupus, but treatments are available to help manage the symptoms. If you think you may have lupus, it is crucial to see a clinician to get an accurate diagnosis and begin treatment as soon as possible.
Some common symptoms of lupus include:
- Fatigue
- Joint pain
- Muscle pain
- Fever
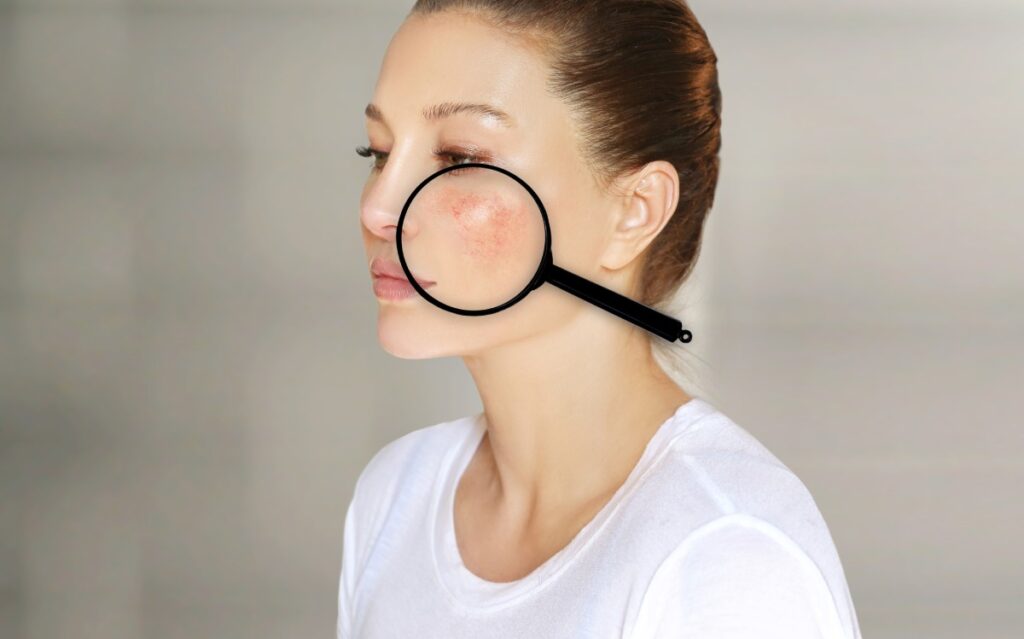
- Rash
- Sun sensitivity
- Mouth sores
- Swelling in the legs or feet
What Causes Lupus?
While the exact cause of lupus is unknown, it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Scientists believe lupus occurs when the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissue, mistaking it for foreign invaders such as viruses or bacteria. This can cause inflammation and damage to different parts of the body.
How Is Lupus Diagnosed?
No single test can diagnose lupus, so doctors often use a combination of lab tests, physical exams, and medical history to diagnose.
Blood tests are often used to help diagnose lupus. These tests can look for signs of inflammation and check for levels of certain immune system cells and proteins. A positive antinuclear antibody (ANA) test is often used as part of the diagnosis process. Still, it’s important to remember that other conditions can also cause a positive ANA test result.
Imaging tests may also be ordered to look for signs of organ damage caused by lupus. For example, X-rays or other scans can be used to assess whether there has been any lung or kidney damage.
Lupus symptoms can be similar to other conditions, so it’s crucial to work with a doctor who is experienced in diagnosing and treating the disease.
How Does It Manifest In The Body?
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect any body part. The human body’s immune system protects against infection and disease. However, in people with lupus, the immune system attacks healthy tissue, causing inflammation and damage. Lupus can affect the joints, skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, blood vessels, and brain. Although lupus can attack almost any system, it does have a predilection for the kidneys and connective tissue.
When lupus manifests in the body, it often does so in the form of a flare-up. A flare-up is a period of time when symptoms become worse. Lupus flares can last for days, weeks, or even months. During an outbreak, people with lupus may experience fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and fever. While there is no cure for lupus, treatments can help manage symptoms and prevent flares. If you think you may have lupus, you must see a doctor for a diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing serious complications.
How Is Lupus Treated?
Lupus is a chronic disease, which means there is no cure. However, treatment can help control symptoms and prevent further damage to the body. Treatment for lupus typically involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. Common medications used to treat lupus include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs – to reduce inflammation
- Corticosteroids – to suppress the immune system
- Immunosuppressants – to suppress the immune system
- Antimalarial drugs – to treat skin and joint problems
The exact type and dosage of medication will be determined by your doctor based on your symptoms and health condition. In addition to medication, people with lupus may also need to make lifestyle changes such as getting enough rest, avoiding stress, and avoiding exposure to sunlight.
What Are The Potential Complications Associated With The Disease Process?
Lupus is a chronic disease that can lead to several severe complications if left untreated. Some of the potential complications associated with lupus include:
- Kidney damage – Lupus can cause inflammation of the kidneys, which can lead to kidney damage.
- Heart disease – Lupus can cause heart inflammation, which can lead to heart disease.
- Lung damage – Lupus can cause inflammation of the lungs, which can lead to lung damage.
- Stroke – Lupus can cause inflammation of the blood vessels, leading to stroke.
How Can You Live A Full Life With Lupus Despite Its Challenges?
Lupus is a chronic disease that can be difficult to manage. However, there are ways to live a full and active life despite its challenges. Some tips for living with lupus include:
Get plenty of rest – Fatigue is a common symptom of lupus, so it is important to get plenty of rest.
Avoid stress – Stress can trigger lupus flares, so it is important to find ways to manage stress.
Exercise – Exercise can help improve fatigue and joint pain.
Eat a healthy diet – Eating a healthy diet can help you manage your weight, get the nutrients you need, and avoid flares.
Are There Any Promising New Treatments For Lupus On The Horizon?
There is no cure for lupus, but several new treatments show promise in managing the disease. Some of the promising new treatments for lupus include:
Biologic drugs – Biologic drugs target specific parts of the immune system.
Stem cell therapy – Stem cell therapy is a new treatment that uses stem cells to help repair damaged tissue.
Clinical trials – Clinical trials are ongoing for many new potential treatments for lupus, including biological drugs and stem cell therapy.
If you or someone you know has lupus, talk to your doctor about the best treatment options. Some new treatments show promise in managing the disease and helping people live full and active lives.
Final Thoughts
The pathophysiology of lupus is still not completely understood, but scientists believe it is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Lupus is a chronic disease that can lead to several severe complications if left untreated. However, there are ways to live a full and active life despite its challenges. If you or someone you know has lupus, talk to your doctor about the best treatment options.